Introduction:
In today's digital age, data privacy and security have become crucial concerns. With the proliferation of online communication, transactions, and storage of sensitive information, protecting data from unauthorized access has become paramount. Encryption has emerged as a vital technology to safeguard data and ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. In this article, we will explore what encryption is, how it works, and why it is essential in today's digital landscape.
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext, which is the original unencrypted data, into ciphertext, which is a scrambled and unreadable form using cryptographic algorithms. The purpose of encryption is to prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized parties with the appropriate decryption key can access the original data. It serves as a safeguard against eavesdropping, data breaches, identity theft, and other security threats.

There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric.
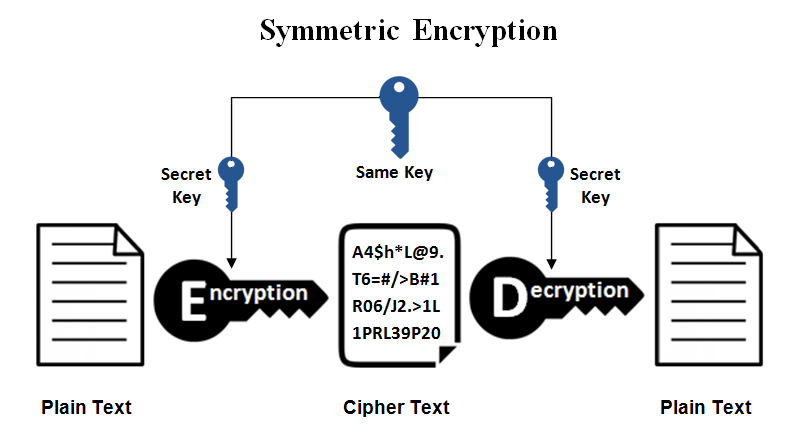
Symmetric encryption:
It uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. The same key is used to encrypt the data at the sender's end and decrypt it at the receiver's end. This type of encryption is relatively simple and fast, but it raises concerns about securely exchanging the encryption key between the sender and receiver without it falling into the wrong hands.
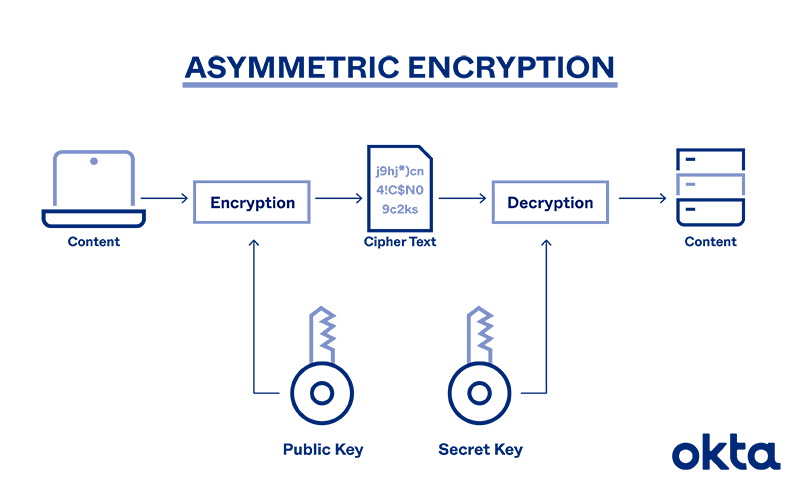
Asymmetric encryption:
It Is also known as public-key encryption, uses two separate keys - a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, while the private key is used for decryption. The public key can be freely shared with anyone, but the private key must be kept secret by the owner. This type of encryption allows for secure communication without the need to exchange a common key, eliminating the key exchange challenge of symmetric encryption.Applications of Encryption:
Secure Communication:
Encryption is commonly used in secure communication protocols such as HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) used for secure online transactions, email encryption, and secure messaging apps. It ensures that the data exchanged between the sender and receiver is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
Data Storage:
Encryption is used to protect data stored on electronic devices such as laptops, smartphones, and cloud storage. It prevents unauthorized access to data even if the device is lost or stolen, providing an additional layer of security.
Financial Transactions:
Encryption is a critical component of online banking and digital payment systems, ensuring that financial transactions are secure and confidential.
Medical Records:
Encryption is used to protect sensitive medical records and patient information, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access the data and comply with data privacy regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Government and Military Communications:
Encryption is extensively used by governments and military organizations to protect classified information, communications, and sensitive national security data from unauthorized access.
Internet of Things (IoT):
As the use of IoT devices continues to grow, encryption plays a crucial role in securing data transmitted between connected devices and ensuring the privacy and integrity of IoT communications.
Encryption is a powerful tool that safeguards sensitive information from cyber threats, identity theft, and data breaches. It ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data, providing an essential layer of protection in today's digital world. However, encryption is not infallible, and it can be vulnerable to attacks such as brute force attacks, key exchange attacks, and side-channel attacks. Therefore, it is crucial to use robust encryption algorithms, keep software and devices up-to-date with the latest security patches, and follow best practices for securely managing encryption keys.
